+86 13794985240
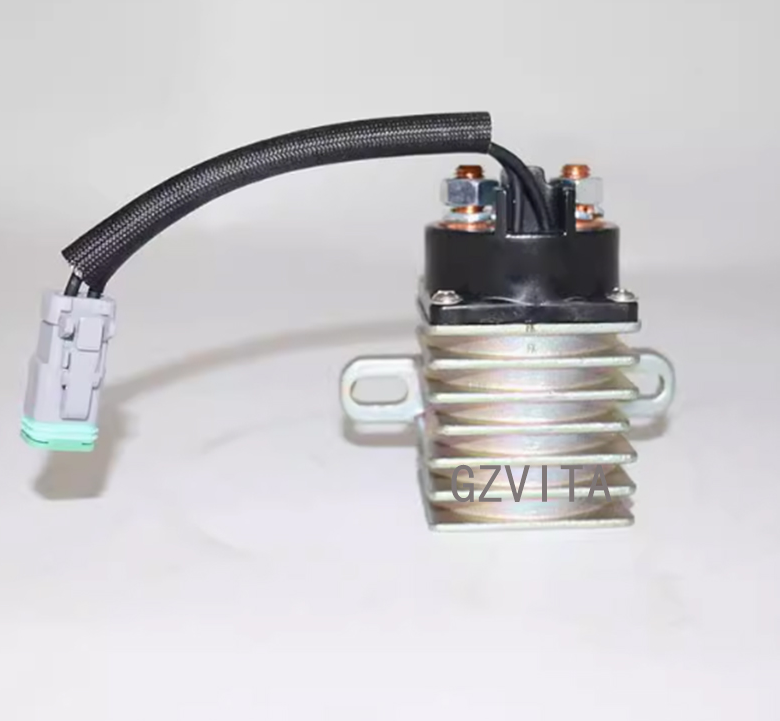
+86 13794985240 What Is The Production Process of Magnetic Switch Assembly?
Here’s an overview of the production process:
- Design and Engineering
Specifications: Define the specifications for the magnetic switch assembly, including voltage ratings, current ratings, and operational requirements.
Prototyping: Create prototypes to test the design and functionality of the magnetic switch.
- Material Sourcing
Components: Source high-quality materials and components, such as magnets, coils, housings, terminals, and circuit boards.
Suppliers: Establish relationships with reliable suppliers to ensure a consistent supply of materials.
- Manufacturing Process
Component Preparation: Prepare individual components, which may include cutting, shaping, and finishing parts.
Winding Coils: If the magnetic switch requires coils, this step involves winding the wire around a core to create the electromagnetic field.
Magnet Assembly: Assemble the magnets in the correct orientation and position to ensure proper functionality.
- Assembly Line Setup
Workstations: Set up workstations for different stages of assembly, such as component insertion, soldering, and testing.
Automation: Consider using automated machinery for repetitive tasks to increase efficiency and reduce labor costs.
- Assembly Process
Component Insertion: Insert components into the housing or circuit board as per the design specifications.
Soldering: Use soldering techniques (manual or automated) to connect electrical components securely.
Quality Control: Implement quality control measures at each stage of assembly to identify defects early.
- Testing
Functional Testing: Test the assembled magnetic switch to ensure it operates correctly under specified conditions (e.g., voltage, load).
Safety Testing: Conduct safety tests to ensure the assembly meets industry standards and regulations.
- Packaging
Final Inspection: Perform a final inspection of the assembled units to ensure they meet quality standards.
Packaging: Package the magnetic switch assemblies securely to prevent damage during transportation.
- Distribution
Inventory Management: Manage inventory levels to ensure timely delivery to customers.
Shipping: Coordinate shipping logistics to deliver the products to clients or distributors.
- Feedback and Improvement
Customer Feedback: Gather feedback from customers regarding the performance of the magnetic switch assemblies.
Continuous Improvement: Use feedback to make improvements in the design, manufacturing process, and quality control measures.
Conclusion
The production line for a Magnetic Switch Assembly (24 V) requires careful planning and execution to ensure high-quality products that meet customer needs. By focusing on design, material sourcing, efficient assembly processes, and rigorous testing, manufacturers can produce reliable magnetic switches that are essential for various applications, including excavators and other heavy machinery.